- Advantages of AS-i
- System integration and set-up
System integration and set-up of AS-Interface
What is needed to get started with AS-Interface?
The master, a power supply unit as well as various standard participants form the basis of every AS-i system. Non-safe participants are also possible (mixed operation). The master ensures data exchange with the participants by means of cyclic polling. The AS-Interface power supply units supply the participants and sensors with energy.
Quick controller integration
AS-Interface systems can be easily connected to different controllers, e.g. from Siemens, Rockwell, Schneider or Omron:
In addition to the hardware, ifm offers startup packages for data connection to the PLC.
PLC startup packages
Use our startup packages to set up AS-Interface systems in combination with industrial controllers from various manufacturers. ifm provides ready-made programming examples and apps.Configuration and setup is considerably facilitated and errors are avoided.
Download the following contents for free:
- setup guide for fast integration into the PLC (Siemens, Rockwell, Omron, Schneider)
- device description files (GSDML, ESI, EDS)
- operating instructions
- example programs for Siemens controllers
- system solution apps such as DTA-RFID, O3D cameras, IO-Link
The required startup packages can be found in the download section of the respective product detail pages:
Addressing your AS-i slaves
Address basics
A total of 32 AS-i basic addresses (0...31) are available for an AS-i system
| Address 0 | Addresses 1...31 |
|---|---|
|
|
Hand-held addressing unit (AC1154)
Modules must be addressed and although the master can be used, the hand-held addressing unit is a good investment.
- Place in the ADDR mode to address units.
- Functions and error codes are listed on the back of the unit.
Addressing a node using the AC1154
- Plug node/valve top into programmer
- Press "Read/On" button to display current address
- Press "+" or "-" buttons to change address to desired number
- Press "Write/Set" to store this address
- Press "Read/On" to confirm
Forcing an output using the AC1154
- Plug node/valve top into programmer
- Press "Read/On" button to display current address
- Press "Mode" button to change LC display in upper left corner to DATA
- Press "+" or "-" until desired HEX code is displayed
- Press "Write/Set" button to energize output(s)
Addressing tools
Automatic addressing
When the AS-i master recognizes a missing AS-i slave from the LDS, connect a new AS-i slave with the same ID/IO to the network. The AS-i master will recognize a new AS-i slave at address 0 and automatically address the new unit to the missing address.
AS-i masters can only auto-address one module at a time. If more than one failure occurs, manually address replacement modules.
Communication basics
- The AS-i master sends the corresponding output information in sequence to each AS-i address
- The slave then responds with its current input information
- The physical order of the slaves on the cable is irrelevant for AS-i communication
- Only the address sequence is decisive
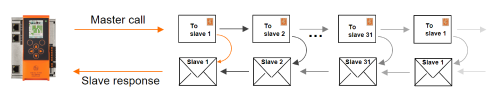
- If an AS-i slave does not respond to a master call, the AS-i master repeats its call immediately. If a master call is not answered, this is called a telegram error
- If the AS-i slave still does not respond, the AS-i master continues with all other slaves first
- After a total of 6 unanswered master calls, the slave concerned is removed from the communication, generating a configuration error occurs
- Every telegram error of each individual slave is counted in the AS-i master for diagnostic purposes